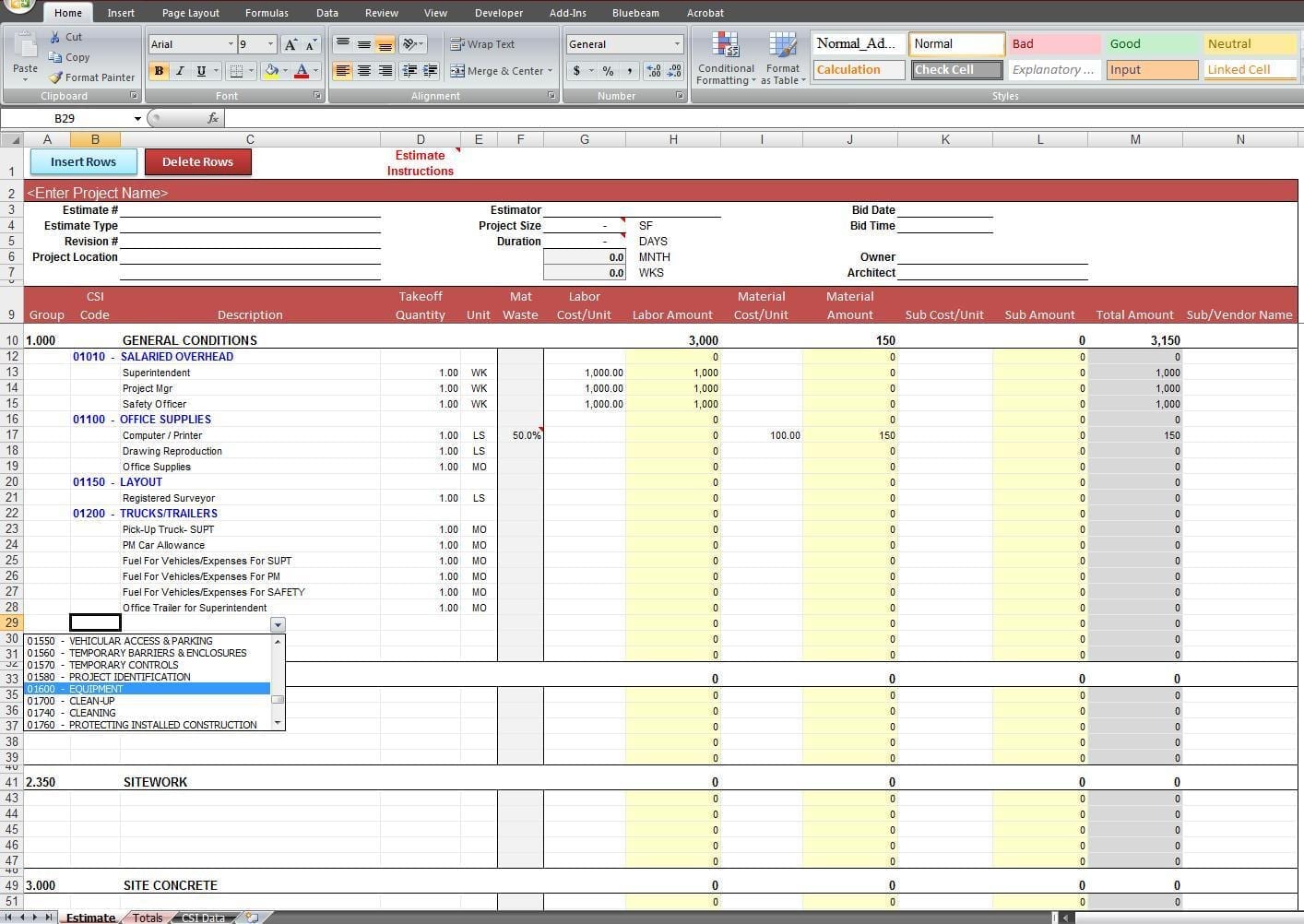
A job cost sheet is a document that lists a job’s components, pricing per unit of a product or service, and final cost. The task order costing system should be used for manufacturing distinctive products. Additionally, this approach is perfect for businesses that provide specialized goods or expensive products like computers or automobiles. Effective job costing practices allow for better cash flow management in construction.
Job Costing in Project Management
Most businesses create annual budgets that include estimated overhead and estimated activity for the year. You can use these budget estimates to calculate an overhead rate to apply to each of your jobs. The predetermined rate is a calculation used to determine the estimated overhead costs for each job during a specific time period. To calculate your predetermined overhead rate, simply divide the estimated overhead by the estimated activity cost. A predetermined overhead rate is an allocation rate used in place of specific overhead costs to make overhead easier to account for.
Job Cost Sheet FAQs
ProjectManager is online project management software that connects teams across departments and time zones, allowing them to share files, comment at the task level and more. Our software allows managers to plan, manage and track more than costs but every aspect of their budget. Join teams at companies such as Avis, Nestle and Siemens who are using our tool to succeed. These can be both direct raw materials that’ll be used in the finished product (usually raw materials) and indirect materials (tools, machinery, office supplies, etc.) that are used to create the product. To calculate the material costs, all the direct material costs with the indirect material costs.
Explore more helpful resources
Unlike job costing which is used in customized manufacturing, process costing is used in standardized or mass-produced manufacturing. When a contractor bids on a project or a manufacturer takes on a job, they need to have an accurate forecast of the price for the project to make a profit, which is why job costing is so important. Calculate how much it costs your business to employ all staff members who will work on the project per day. The direct labor costs calculation involves multiplying the payroll day rate by the amount of time you estimate you’ll need to complete the job. If you rely on subcontractors to complete work your company doesn’t do itself, factor those costs into your total labor costs for the job.
How Are Job Cost Sheets Calculated?
The expenses shown below were incurred for a job during the year ended on 31 March 2019. A supervisor will also be paid a flat rate of $3,500 for the entire project. You receive a work order to fix a broken faucet at one of your customers’ properties. JD enjoys teaching people how to use ZoomShift to save time spent on scheduling.
Job Costing: What It Is & How To Calculate It
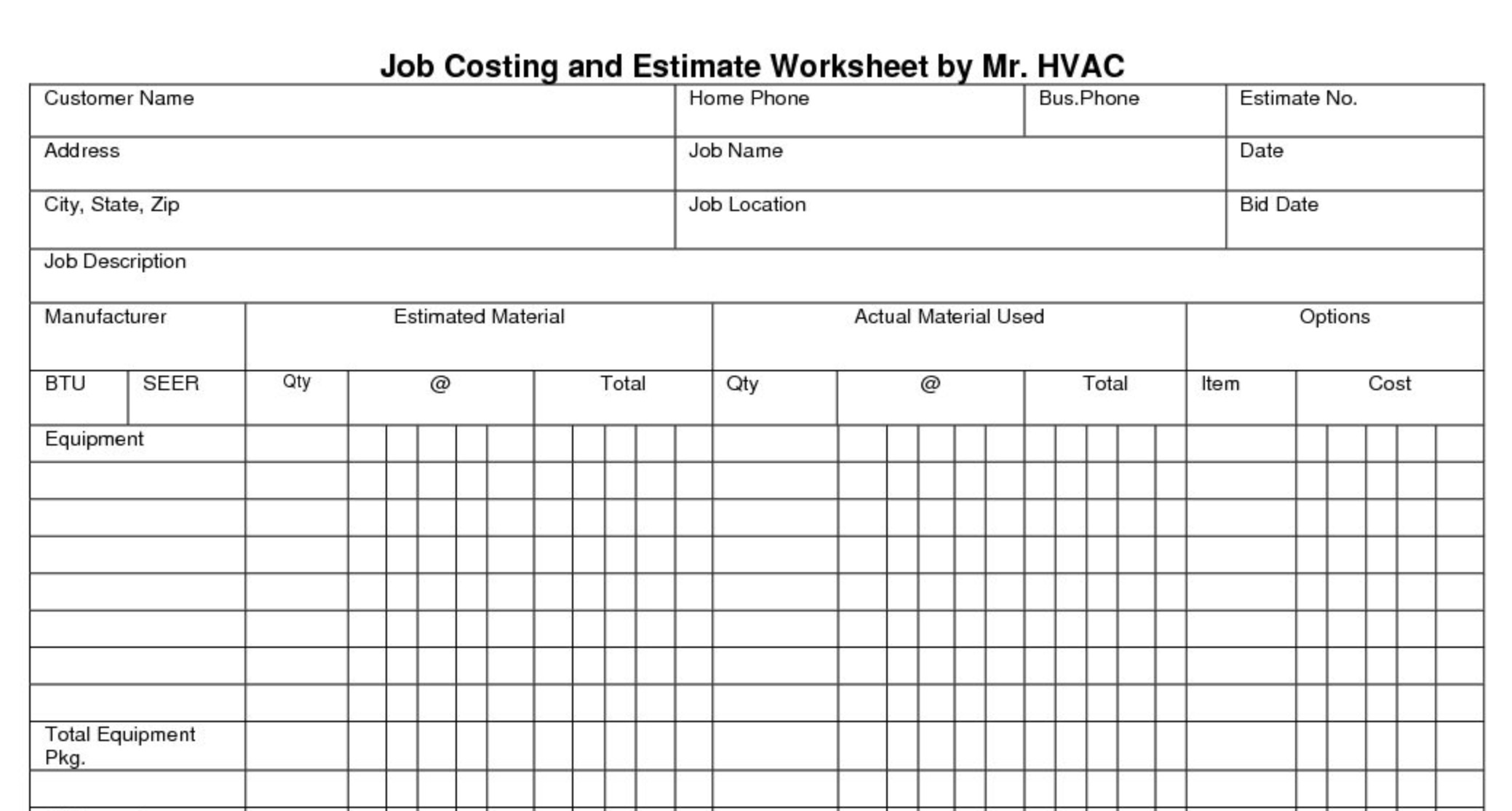
Process costing could be used, for example, to track the cost of each identical pack of gum produced over the course of 6 production months. Thankfully, Field Promax allows you to run reports as frequently as you like. What was formerly a cost-tracking process can now be transformed into a wealth of information that can guide your project’s execution.
To avoid delays in distributing overheads on an actual cost basis, overheads are generally charged at predetermined rates (i.e., the rates worked out based on the previous period’s figures). Job costing is a system in which costs are assigned to batches or work orders of production. That’s five people at $100 a day per person, with a duration of three days to make the hole. Again, this is a five-person job at $100 per day per person, with a duration of two days.
Because these costs are indirect to the project itself, overhead costs are the most difficult to track. Wages for employees working indirectly on a project (supervisors, custodians, etc.) should be tracked under overhead costs. Job costing is commonly used in project-based businesses such as construction companies, advertising and marketing agencies, medical offices, law firms, and more.
- It is particularly useful for project managers in various industries to accurately track and allocate costs, as well as to make informed decisions regarding pricing, resource allocation, and budget management.
- If you’re starting a new business, make sure you fully understand how to calculate the costs involved with your work so that you don’t end up losing money instead of making it.
- A predetermined overhead rate is an allocation rate used in place of specific overhead costs to make overhead easier to account for.
- You’re excited at the new prospect and sit down to come up with a reasonable but competitive quote.
- It also allows them to benchmark themselves against the competition to uncover areas that can be improved and make them more competitive.
For instance, the cost of transporting materials can be divided among projects based on the quantity of materials used in each one. To begin job costing, the estimator creates a cost breakdown for each project. The scope of work is broken down into categories or activities required by the project. Though different accounting for capital rationing and timing differences types of projects require specific breakdown structures, the process for breaking down expenses remains the same. Job costing is a beneficial practice for any industry, offering a detailed view of all potential project costs. This insight enables businesses to better anticipate expenses and prepare accordingly.
By comparing actual expenses against budgeted amounts continuously, project managers can ensure that the project remains financially on track. This real-time budget monitoring is critical in an industry where even small financial missteps can have significant impacts on profitability. Job costing is a method of cost accounting used to determine the cost of producing a specific job or project. It is particularly useful for project managers in various industries to accurately track and allocate costs, as well as to make informed decisions regarding pricing, resource allocation, and budget management. Overhead is the most difficult cost to calculate because you’ll need to rely on an approximation instead of the actual cost. You’ll need to accurately estimate the total overhead costs factoring into the job, including rent on your office, administrative costs, and depreciation, or machine hours, on the equipment used.
